Translated from the ancient Greek language, osteochondrosis means ὀστέον - bone and χόνδρος - cartilage and is characterized by complex degenerative changes in the articular elements of the bone skeleton. Almost every part of the skeletal framework is susceptible to this neurological disease. There may be thoracic and / or cervical spinal discs in the affected area. It is osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, whose symptoms and treatment are most common in modern conditions, is the cause of discussion and concern of practicing neurologists.
Pathogenesis or development of the inflammatory process
Every organism in the process of growth changes its physiology. Thus, diffuse changes occur in the vascular bed of the intervertebral discs of the skeleton. The supply of nutrients to the lumbar spine is complicated by various traumatic conditions and / or constant dynamic loads on this part of the spine. Insufficiency in the nutrition with the necessary microelements is further complicated by osteochondrosis processes, leading to loss of elastic and healthy characteristics of the cartilage joints. In osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the symptoms of the disease are most active in asymmetric and irrational work of the muscles of the spine, which are found in different conditions:
- insufficient heating of muscle tissue;
- improper posture;
- congestion of the intervertebral joints due to excess adipose tissue;
- use of mattresses on a soft base during a night's rest;
- acute mechanical and / or dynamic loads on the lumbar spine;
- physical stress;
- with exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
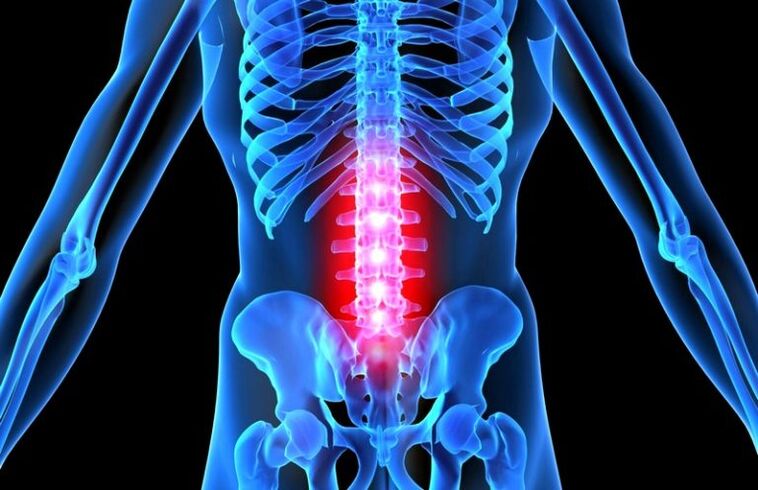
The supply of nutrients to the lumbar spine is complicated by various traumatic conditions and / or constant dynamic loads on this part of the spine.
If lumbar osteochondrosis is detected, the symptoms of a neurological disease due to untimely medical intervention can lead to more serious neurological pathologies, such as sciatica, spinal hernia, damage to the intervertebral discs and other complications.
Why does lumbar osteochondrosis occur?
To date, the problem of diffuse transformations in the intervertebral space has not been fully studied. In osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the symptoms of neurological pathology are often felt by people aged 35 to 45 years.

Nervous overload, stressful situations can also lead to the appearance of the disease.
At this most effective age, static and dynamic stress occurs on the spine. However, according to expert observations, back pain is beginning to worry more and more people in the younger age group. So, between the ages of 18 and 25, young people become patients in neurological wards. This is due to poor physical activity, overweight, poor posture and general deformity of the joints that cause lumbar osteochondrosis.
Symptoms and treatment of neurological pathology, it is desirable to identify and adequately respond to it at the earliest stage of disease formation.
Other causative factors leading to lumbar osteochondrosis include:
- hereditary forms;
- insufficient supply of micronutrients to the cartilage vessels;
- disturbance of metabolic processes due to various circumstances;
- uneven development of the musculoskeletal structure;
- sedentary way of life;
- disorders of the body related to the functioning of the endocrine system;
- weakening of muscle structures due to the harmful effects of alcohol, smoking and other bad habits;
- consequence of various chronic pathologies;
- segmental instability of the elements of the spine;
- nervous overload, stressful situations and other components.
However, when osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine is diagnosed, the symptoms of neurological pathology in women can be diagnosed due to disorganization or the development of disorders associated with hormonal changes. At the age of 35 to 45 years, the female body begins to undergo significant physiological transformations, which affects the functional work of all bone and cartilage areas of the spine.
Symptomatic signs of the disease
In osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region, the symptoms of neurological pathology are felt with pain in the lumbar region, which leads to tingling, discomfort and a feeling of pain in the lower back. Lack of appropriate adequate therapy can complicate the situation and lead to complete atrophy of the muscular structures in the lumbosacral spine. The increase in pain can be provoked by various factors, such as sneezing, coughing, sharp turns and lifting heavy objects. The cuts that appear in the lumbar region are most often given to the gluteal region and the calf area of the lower limb. In lumbosacral osteochondrosis, the symptoms of a neurological disease can be determined by the following signs:
- discharge of acute painful pain in the sacral spine and pelvic organs;
- loss of sensitivity;
- discomfort in the innervated muscles of the lumbar spine;
- hypotension and malnutrition.

All these symptomatic signs arise from damage to the nerve roots in the intervertebral discs of the lumbar spine.
Stages of the disease
When diagnosing lumbosacral osteochondrosis, the symptoms and treatment of the disease depend on the stage of the inflammatory process. So, according to the results of a diagnostic examination, it is possible to identify several specific signs of inflammation of the lumbar spine:
- The first stage is determined by mild pain in the lumbar region, which intensifies under the influence of exercise. Only with sharp movements, the patient feels sharp, painful or dull pain in the lower back. In a relaxed state, the pain does not appear.
- The second stage is determined when the distance between the spinal discs decreases due to compression and the appearance of degenerative-dystrophic formations in the fibrous ring. Cutting sharp pain radiating to the ankle of the lower limb, buttocks and outer thigh, is due to compression of the nerve endings between the discs in the spine.
- The destruction of the fibrous ring occurs in the third stage of the disease and this is the most favorable moment for the formation of a hernia in the intervertebral disc. Intense pain in the lumbar region is constant due to significant deformation in the lumbosacral spine.
- The last, fourth stage of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, whose symptoms, treatment and rehabilitation are the most difficult in the whole process of destruction of the musculoskeletal system. This stage of the disease leads to injury to the patient, as well as to complete or partial immobilization.
However, any form of osteochondrosis should not cause fear and panic in humans; only appropriate adequate medical treatment is required.
Lumbar osteochondrosis: symptoms and medications
Based on the results of symptomatic signs and the establishment of an appropriate diagnosis according to the stage and form of the disease, specialists select the appropriate drug treatment, which is based on the use of pharmacological combinations with different targets. The main treatment goals in solving the problem are:
- slowing down the degenerative-dystrophic processes in the lumbar area by applying appropriate therapeutic and prophylactic measures;
- elimination of functional disorders of the spinal nerve endings;
- neutralization of painful sensations;
- functional restoration of muscle tone of the lumbosacral region;
- returning the patient to an active life.
The age and sex of the patient, as well as the condition of his endocrine system, play a significant role in choosing a method of drug treatment.
The main emphasis in drug exposure is on pain relief with an appropriate choice of pharmacological analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs allow you to neutralize the destructive processes in the muscular structures of the spinal region. The most effective pharmacological agents are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory groups.

The most effective pharmacological agents are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory groups.
In case of ineffectiveness of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), anesthetics with hormonal supplements and / or paravertebral blockade are used. In addition, the complex drug process includes other types of pharmacological drugs, such as sedatives, muscle relaxants, drug groups containing vitamins B1 and B12, which eliminate the compression effect and ensure the supply of micronutrients to nerve tissues. After the end of the acute inflammatory period, the treatment with drug therapy is completed and other therapeutic and prophylactic measures are applied during the period of remission.
Therapeutic prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
You should know that the treatment of osteochondrosis is a complex process that requires strict discipline and strict adherence to all prescriptions of the attending physician. Prerequisite for complete recovery of the body is the conduct of all stages of complex therapy, which includes:
- Massage that helps relieve muscle pain, restore blood circulation in problem areas of the lumbar spine, eliminate muscle tension in these areas of the body.
- Physiotherapy is a great way to rehabilitate after an illness. The lack of side effects, the removal of residual stresses in the lumbar region, these are the advantages of physiotherapy procedures.
- Manual therapy is able to mechanically affect the muscle tissues of the lower back in a measured measure and provide them with improvement in all vital processes.

It should be remembered that non-compliance with the recommendations of the neurologist for the complex therapeutic treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis is a possible meeting with the surgeon. In 90% of cases, the surgery in the spinal departments is a consequence of a neglected condition of the disease and non-compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician.

























